Store Operations: Product Pricing Strategy

1 Introduction
For some cross-border sellers, pricing their products in cross-border e-commerce can be a significant challenge because the reasonableness of product pricing directly affects the conversion rate of orders.
Therefore, product pricing is a crucial aspect of cross-border e-commerce store operations. It is influenced by various factors, including product costs, market demand, competitor pricing, promotional conversions, and more.
Our editor frequently receives inquiries from sellers regarding pricing-related issues. After selecting products on BuckyDrop, how should you determine the pricing? How can you strike a balance between sales volume and profit?
The image below provides a simulated example of product pricing based on product categories and sales regions for your reference.
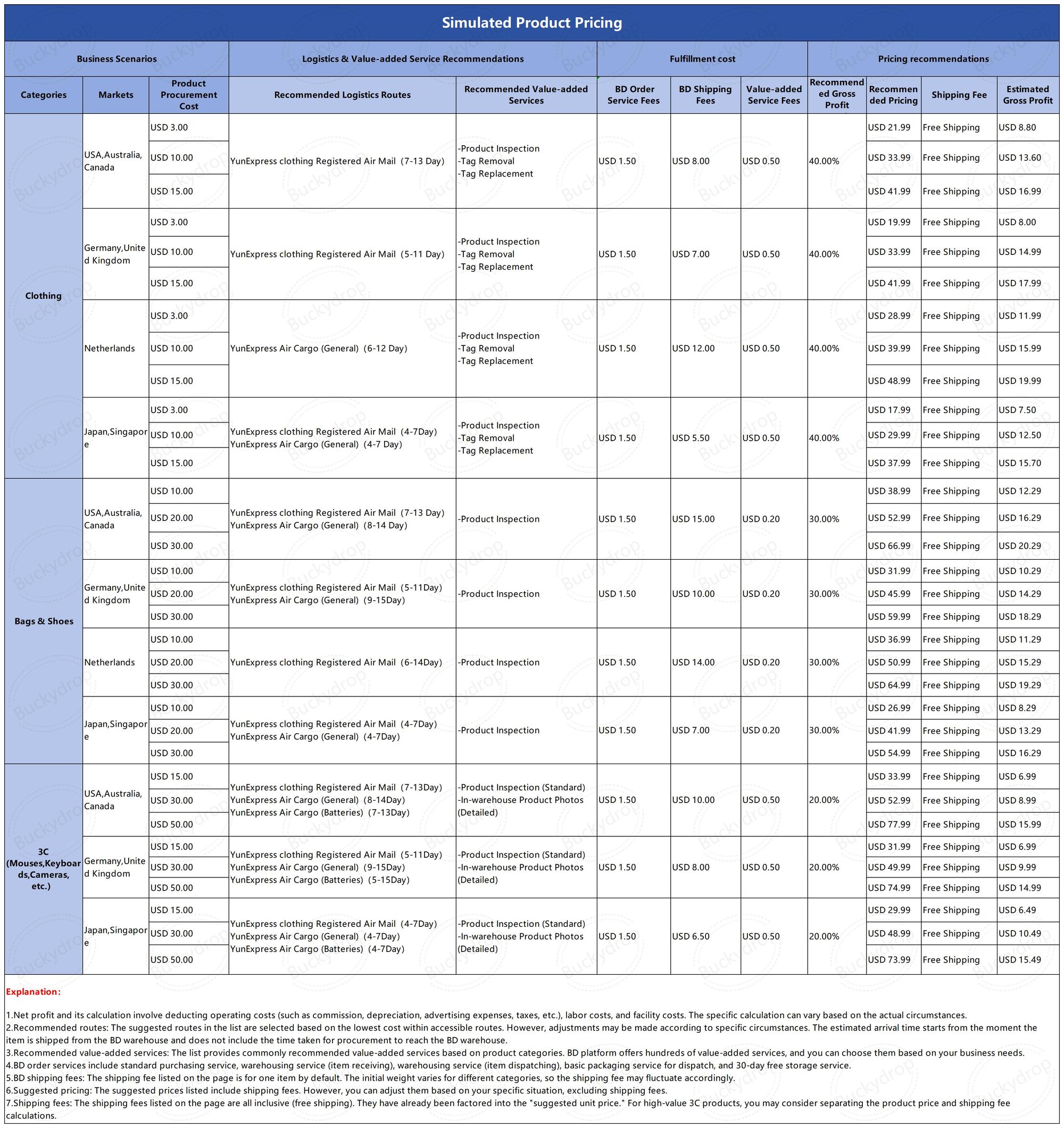
2 Cost and Profit Calculation
2.1 Cost Estimation
Before pricing a product, it is important to understand its cost. Costs are generally divided into three parts: product procurement and fulfillment costs, store operation costs, and labor and facility costs.
Product procurement and fulfillment costs are directly reflected in the process of order fulfillment. In the case of dropshipping, this mainly includes product procurement costs, fulfillment service fees, and shipping fees.
Store operation costs typically include advertising, store setup costs, and platform fees/commissions. These costs are usually settled on a monthly or annual basis and need to be allocated based on the sales volume of the store.
Let's take an example of a Shopify store using BuckyDrop for one-item dropshipping to calculate all the costs involved.
A. Product Procurement Cost

B. Store Operation Costs

C. Labor and Office Space Costs
Based on the above diagram, we can derive the formula for the total cost of goods sold.
Total Cost of Goods Sold = Cost of Goods Purchased + Store Operation Costs + Labor and Facility Costs
2.2 Gross profit margin
In setting the pricing of goods, you also need to consider how to establish a reasonable gross profit margin, ensuring that it satisfies your profit requirements without negatively impacting sales due to excessive pricing.
Different product categories have different gross profit margins, which should be determined based on various factors such as market competition, buyers' acceptable price ranges, and costs. Generally, the gross profit margin is set between 10% and 50% of the product's selling cost.
2.3 Example of Product Pricing
Based on the previous explanation, we can derive a formula for product pricing:
Product Price = (Product Procurement Cost + Store Operation Cost + Labor and Facility Cost) /(1 - Gross Margin)
However, since the store operation cost and labor and facility costs may vary for each store, it is not feasible to calculate them based on specific monetary ratios. Therefore, we will not include them in the calculation here. You can distribute these costs into your gross margin setting according to your actual situation. Therefore, a simplified formula can be used:
Product Price = Product Procurement Cost /(1 - Gross Margin)
Please note that this simplified formula serves as a starting point. In practice, it is recommended to perform more detailed pricing calculations and analysis based on the specific business context and cost structure.
Let's calculate the pricing for a piece of clothing that is shipped for free to the United States, following the example you provided. You purchase the clothing item from BuckyDrop for USD10, list it on your Shopify store, and sell it in the US. The shipping cost is USD10, and you expect a gross margin of 50%.
We can use the formula below to calculate the price:
Product Price (with free shipping) = (USD10 (product procurement) + USD10 (shipping cost) + USD1.5 (fulfillment fee))/(1-50%)
Product Price (with free shipping) =USD43
If after monthly analysis, the store operation cost and labor/ facility cost are averaged to be USD15 per order, the current net profit for the product is USD6.5 with a net profit margin of 15%.
3 Pricing Strategy
After introducing the key elements of product pricing, let's now recommend some different pricing strategies for selling products at various price points.
3.1 Low-priced products (USD0.1-USD20)
3.1.1 Introduction and Explanation
let's talk about low-priced products. Low-priced products refer to goods priced between USD0.1 and USD20. When setting the prices for these products, there are three key points to consider:
A. Shipping Fees: Since the product price is low, consumers are highly sensitive to shipping fees. Typically, the shipping fee for low-priced products should not exceed the unit price of the item. If it surpasses the unit price, it will make sales more challenging.
B. Sales Objectives: The primary objective for low-priced products is to sell as many units as possible. By offering a low price, you aim to entice visitors into making impulse purchases, thereby increasing traffic.
C. Marketing Costs: You should allocate around 30% of the retail price as marketing costs for your product. This cost may vary depending on the price of your product. After all, making a decision to purchase a USD100 product requires more consideration compared to a USD5 product. Therefore, more expensive products necessitate a larger marketing budget.
For low-priced products, we recommend using two pricing strategies: fixed amount free shipping and bundle pricing.
3.1.2 Fixed amount free shipping
Fixed amount free shipping to reaching a set order amount to have the shipping fee waived. When setting prices, it is necessary to allocate the shipping cost evenly among the unit prices of the products and calculate the amount needed to reach for free shipping.
The advantages of this pricing strategy are that customers tend to add more items to their carts in order to qualify for free shipping, increasing the likelihood of purchasing other products from the store. Additionally, offering free shipping creates a sense of getting a good deal in the customer's mind.
However, there are also drawbacks to consider. Setting a high enough order amount for free shipping may result in higher individual product prices, which could lead to customer churn. Therefore, when implementing the free shipping threshold, it is crucial to clearly indicate this information to customers.
By providing clear indications and benefits of free shipping, customers are more likely to pursue the offer and make additional purchases, ultimately benefiting the store.
Let's take an example of a clothing item sold on BuckyDrop and explore how to set pricing using the Fixed amount free shipping.
The purchase price of the product ranges from USD1.23 to USD3.45, which is very attractive. However, the cross-border shipping fee is close to USD8, which is more than twice the highest purchase price. If we calculate the pricing separately for unit price and shipping fee, it would result in the shipping fee being higher than the product's unit price. Therefore, for these low-priced products, we recommend sellers to use the "Fixed amount free shipping" strategy.
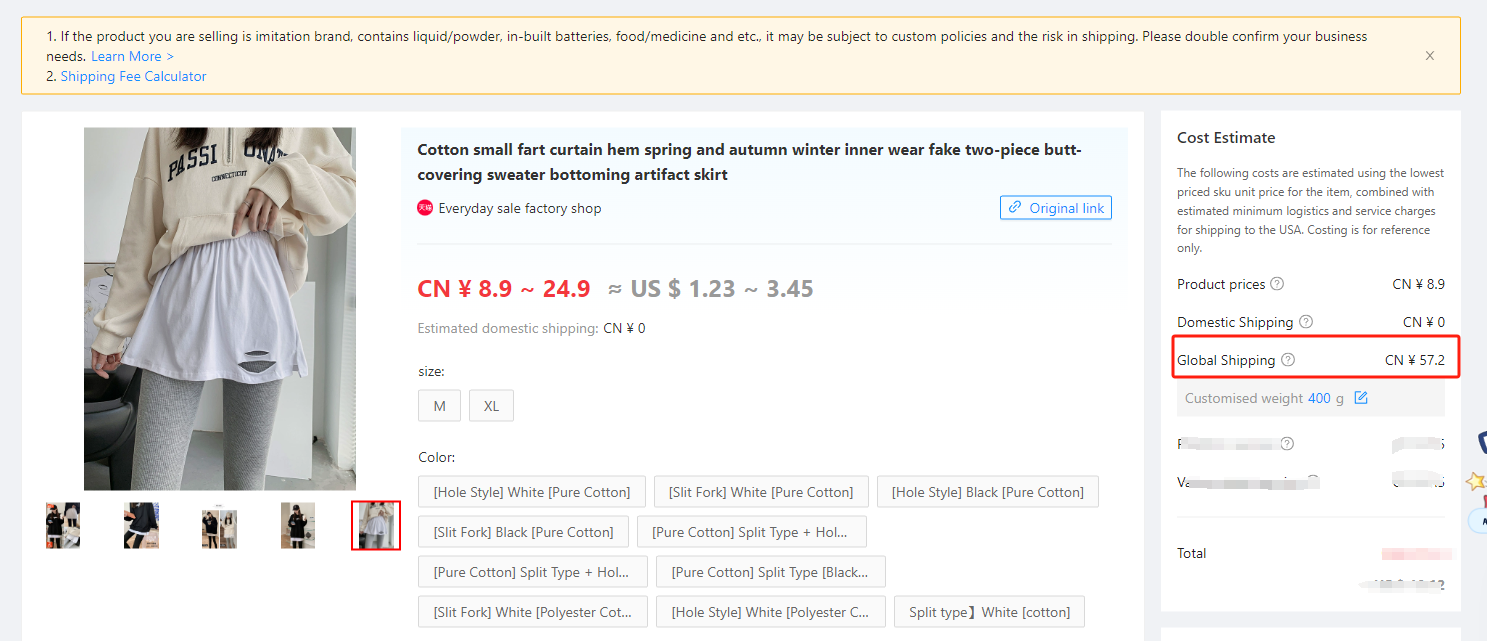
To calculate the optimal amount for free shipping, set the product price, and determine the net profit based on the estimated 50% gross profit margin, you can follow these three steps:
Step 1: Calculating the cost of product procurement
A. Shipping Fee
You can use the estimated shipping cost test on the BuckyDrop product detail page. The shipping cost for sending one item (weighing 400g) to the United States is approximately USD8, but the shipping cost for sending eight items (weighing 3200g) to the United States is approximately USD33. On average, the cost of shipping per individual package has decreased by

Note: In the example provided, the selected shipping option is "YunExpress clothing Registered Airmail," which offers the lowest shipping cost under BuckyDrop. If you require faster delivery, you can opt for the "Mainland China UPS" logistics service available on the platform. However, please note that this option will come with relatively higher costs.
B. BD Order Service Fees
Apologies for the confusion. The fulfillment handling fee for BuckyDrop is approximately USD1.5 per package. If the purchase includes the same product, which counts as one package, then with 8 packages, the total fulfillment handling fee would indeed be USD12.
C. Total cost of product procurement
The purchase cost of the goods is calculated based on the highest unit price of USD3.45.
The purchase cost for 8 units of the product is USD27.6.
Total cost of product procurement= USD33 (shipping fee) + USD12 (insurance service) + USD27.6 (product purchase cost) = USD72.6.
Step 2: Calculate Free Shipping Amount
The total amount for Calculate Free Shipping Amount
Calculate Free Shipping Amount = USD72.6 (product cost) /(1-50%) Gross Profit Margin= USD145.2
Step 3: Calculate Product Unit Price
Product Unit Price=Calculate Free Shipping Amount/8=USD145.2/8=USD18.15
Based on the comprehensive calculation above, it can be concluded that free shipping is available for orders with a total amount of USD145.2 or higher. The unit price of the product is set at USD18.99.
Note:
1.When setting up the free shipping threshold, it is important to consider the weight. In the example provided, the shipping cost was calculated for weights below 3200g. Additional charges will apply for weights exceeding this limit.
2.The amount for free shipping should not be set too high to avoid discouraging potential customers.
3.Consider adding low-priced products to encourage customers to reach the free shipping threshold.
4.For products eligible for free shipping, it is recommended to use cost-effective shipping routes available on BuckyDrop, such as "YunExpress clothing Registered AirRoMail" and other similar logistics options.
3.1.3 Bundle pricing
Bundle pricing refers to the practice of combining different products together for sale, which can include combinations of similar items, sets, accessories, and more.
The advantages of bundle pricing include increasing sales revenue while indirectly reducing shipping costs. It also allows for an increase in profit per order.
For example, if a pair of pants is priced at USD10 and a shirt is priced at USD20, by offering them as a bundle, the combined price could be set at USD30. If the shipping cost is USD10 and does not exceed the total value of the items, it becomes more advantageous for sales.
3.2 Mid-range products (USD20-USD50)
For mid-range products, as the price of the product is relatively high, the shipping cost tends to have a lower proportion in the total cost of the order. In this case, a strategy of separately calculating the product price and shipping cost can be used.
The advantage of separating the product price and shipping cost calculation is that it allows for a lower product price, which can attract buyers. However, the disadvantage is that customers may be deterred if the shipping cost exceeds their expectations. It also increases the cognitive cost for customers to calculate the total cost including shipping.
Taking an electronic product on BuckyDrop as an example, with a starting procurement cost of USD30.33, logistics cost of around USD7, fulfillment handling fee of USD1.5, and targeting the US market with the desired gross profit margin of 20%, the pricing and shipping cost can be calculated in the following three steps.
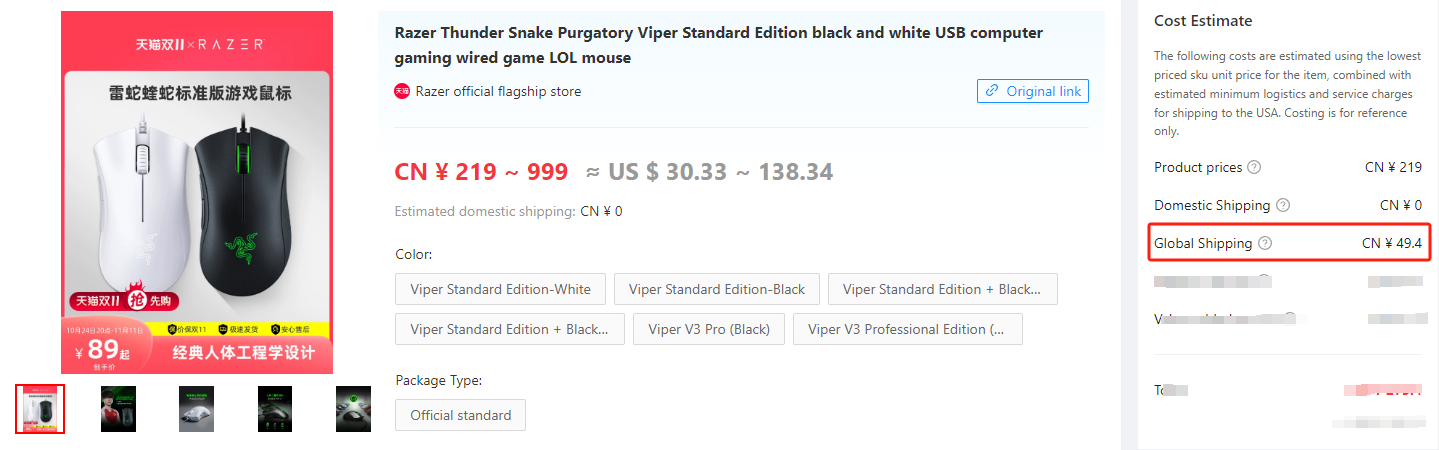
Step 1: Calculating the cost of product procurement
Calculating the cost of product procurement= USD30.33 (product procurement cost) + USD1.5 (fulfillment handling fee)= USD31.8
Step 2: Calculate Product Unit Price
Calculate Product Unit Price=Calculating the cost of product procurement/(1-Gross Profit Margin)=USD31.8/(1-20%)= USD39.75
Step3: Shipping Fee
By utilizing the "Shipping Fee Calculator" tool developed by BuckyDrop, you can calculate the shipping cost per gram and explore available routes. It is advisable to add around a 20% markup, although the specific amount may vary depending on your store's circumstances.
3.3 High-priced products (greater than USD50)
For high-priced products, due to their higher price range, it is recommended to use fixed markup or competition-oriented pricing strategies.
Taking an electronic product on BuckyDrop as an example, this standardized electronic product faces intense market competition, with transparent pricing for similar goods. Therefore, products like these are more suitable for fixed markup or competition-oriented pricing strategies.
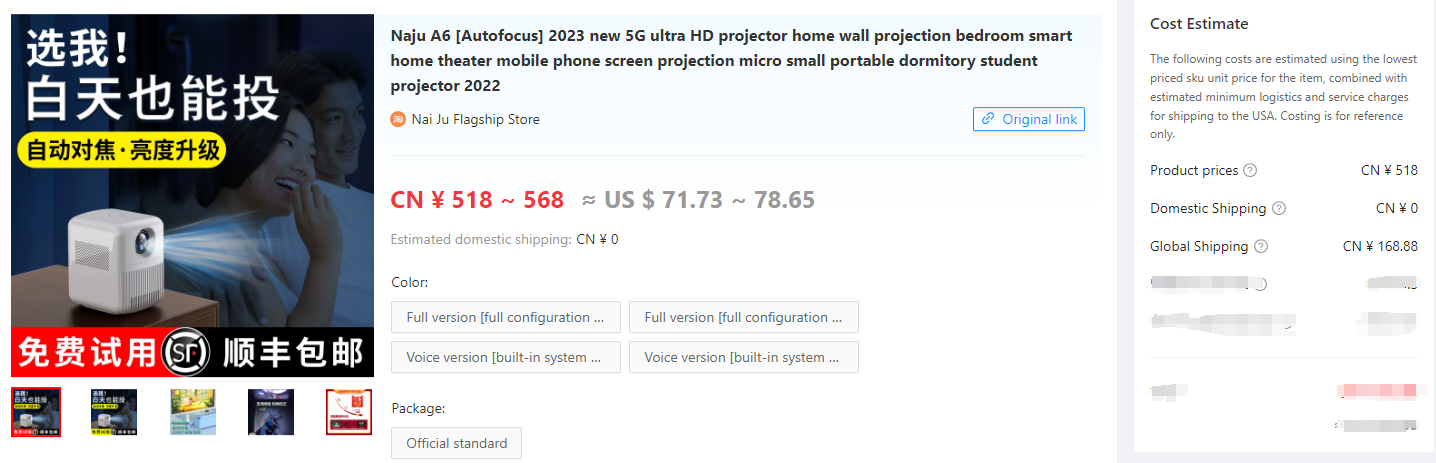
3.3.1 Fixed Markup Strategy
Product procurement cost: USD71.7
Shipping cost: USD27
Fulfillment handling fee: USD1.5
Total procurement cost: USD100.2
Fixed markup: USD50
For high-priced products, a free shipping strategy can be used. The selling price with free shipping would be USD150.2.
It is recommended to use the "Mainland China UPS" logistics option available on the platform for high-value products. This option offers faster delivery, reaching customers within 3-5 days. However, it may come with a higher shipping cost of approximately 30% compared to regular logistics.
The advantages of a fixed markup strategy include consistent profits, simplified operational calculations, and lower perceived costs by buyers.
The downside is the lack of flexibility, limiting adjustments in pricing for future promotional activities.
3.3.2 competitive pricing strategies
By searching for pricing of similar products within the same platform or across platforms, you can develop a competitive pricing strategy that either follows or sets prices lower than those of your competitors, while ensuring acceptable profit margins.
The advantages of competition-oriented pricing strategy lie in closely tracking competitors, making it easier to secure orders. However, the downside is the possibility of getting caught up in price wars.
4 Conclusion
The above are some commonly used pricing strategies for products, provided for reference. They can be adjusted based on the actual operational situation of the store. If there are better strategies in the future, they will be continuously updated.
Learn More
➜ Contact Us: marketing@buckydrop.com



